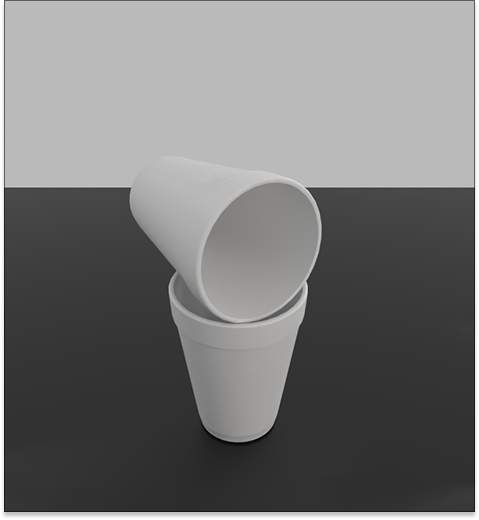
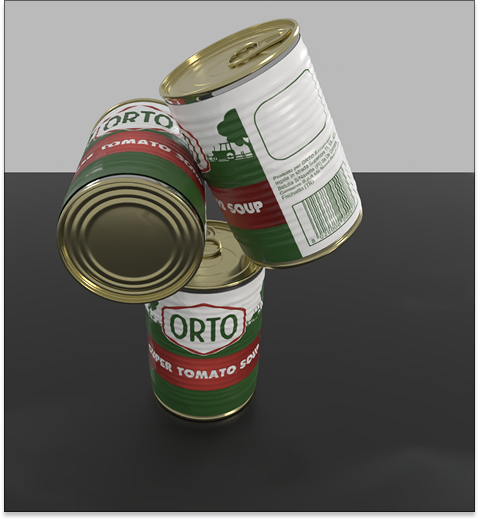
PhyScensis: Physics-Augmented LLM Agents for Complex Physical Scene Arrangement
ICLR 2026
Abstract
Automatically generating interactive 3D environments is crucial for scaling up robotic data collection in simulation. While prior work has primarily focused on 3D asset placement, it often overlooks the physical relationships between objects (e.g., contact, support, balance, and containment), which are essential for creating complex and realistic manipulation scenarios such as tabletop arrangements, shelf organization, or box packing. Compared to classical 3D layout generation, producing complex physical scenes introduces additional challenges: (a) higher object density and complexity (e.g., a small shelf may hold dozens of books), (b) richer supporting relationships and compact spatial layouts, and (c) the need to accurately model both spatial placement and physical properties. To address these challenges, we propose PhyScensis, an LLM agent-based framework powered by a physics engine, to produce physically plausible scene configurations with high complexity. Specifically, our framework consists of three main components: an LLM agent iteratively proposes assets with spatial and physical predicates; a solver, equipped with a physics engine, realizes these predicates into a 3D scene; and feedback from the solver informs the agent to refine and enrich the configuration. Moreover, our framework preserves strong controllability over fine-grained textual descriptions and numerical parameters (e.g., relative positions, scene stability), enabled through probabilistic programming for stability and a complementary heuristic that jointly regulates stability and spatial relations. Experimental results show that our method outperforms prior approaches in scene complexity, visual quality, and physical accuracy, offering a unified pipeline for generating complex physical scene layouts for robotic manipulation.
Methodology Overview
Our framework consists of three components:
(a) an LLM agent that takes a user prompt and generates spatial and physical predicates, along with object descriptions for retrieval.
(b) a solver that computes the final scene using a physics engine for physical predicates and a sample-based constraint solver for spatial predicates.
(c) a feedback system that reports success or diagnoses failure, allowing the LLM agent to iteratively refine and regenerate predicates.
Qualitative Results
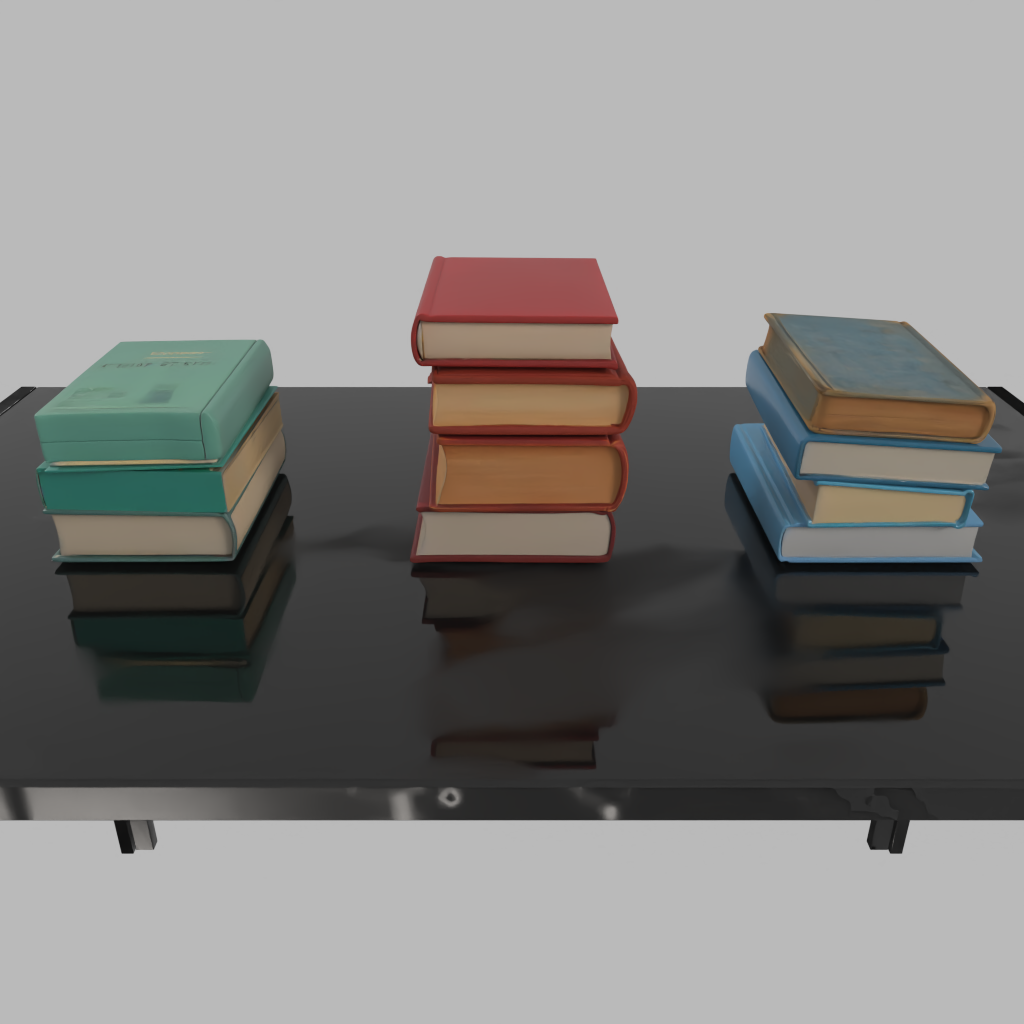
Strong Controllability over Textual Descriptions
3 stacks of books, each with 3-4 books where the books in each stack are visibly different from each other but all have roughly the same color within each stack.

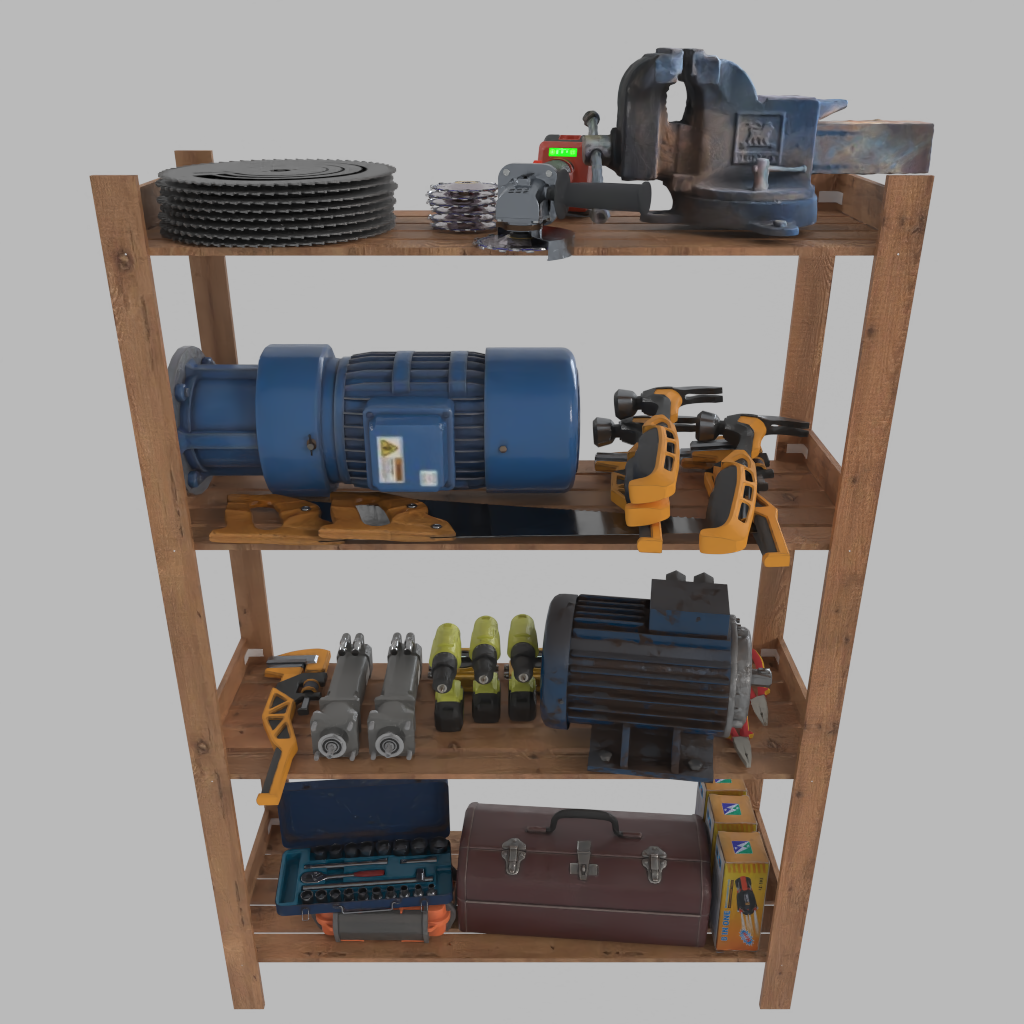
Layer 1: Place 1 red toolbox, 1 orange toolbox, and 3 yellow toolbox on the shelf. Another blue toolbox should be place on the orange toolbox.
The red one should be placed in the middle of the shelf and the orange one should be on the right.
The three yellow toolbox should be placed in an organized manner, align in x axis, and placed to the left most of the table.
Layer 2: Place 3 drills in the middle, aligned, facing front. To the left is a middle-size blue motor and to the right is 2 small black motors.
At last, place 1 wrench and 2 pliers randomly.
Layer 3: Place a large electric motor in the right-back part of the shelf. Then place 2 hand saw, 3 wrench and 3 hammer randomly in the remaining place.
Layer 4: Place a blacksmith jaw with random rotation. Then place a stack of 8 circular saw blade on the right of the shelf. In the middle is a angle grinder, facing front. Near it is a stack of 6 grinder chain discs.

Scene Generation for a Given Prompt
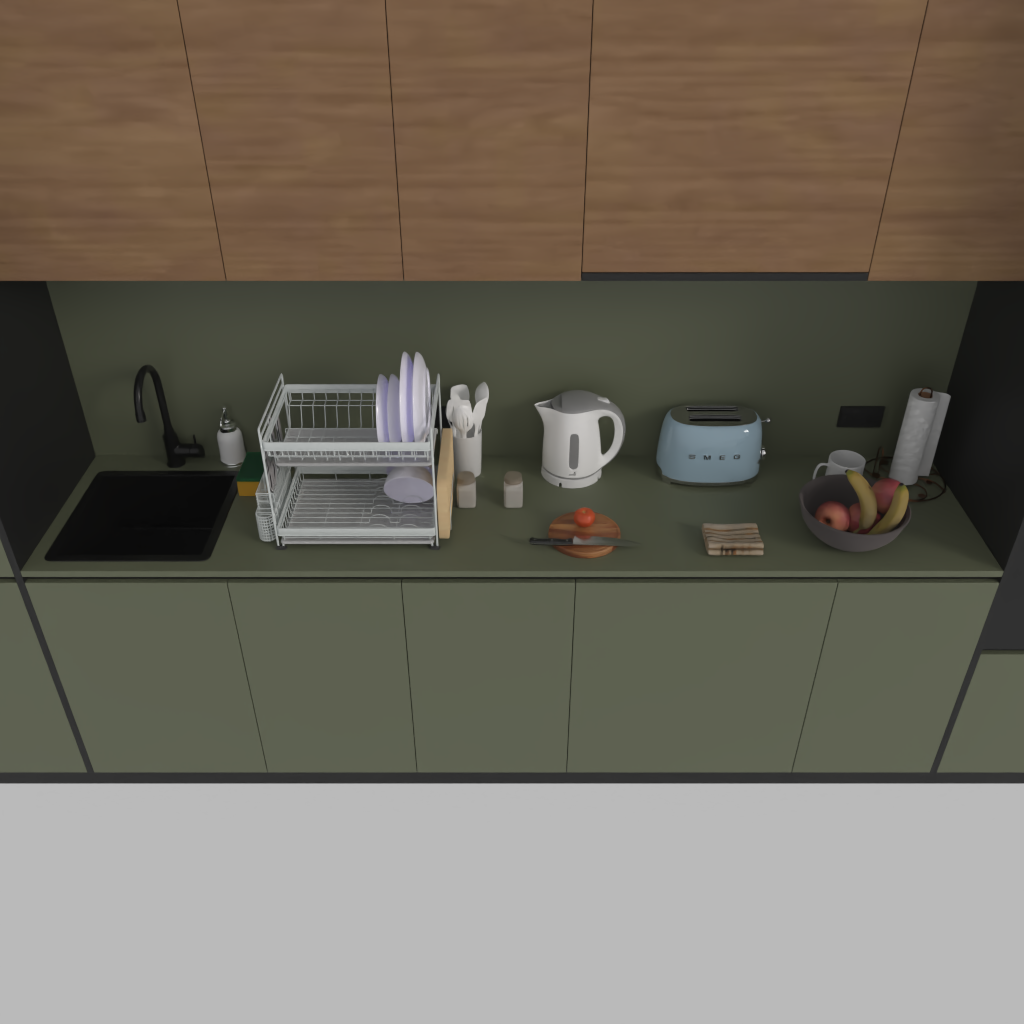
The working desk of a computer science PhD student.
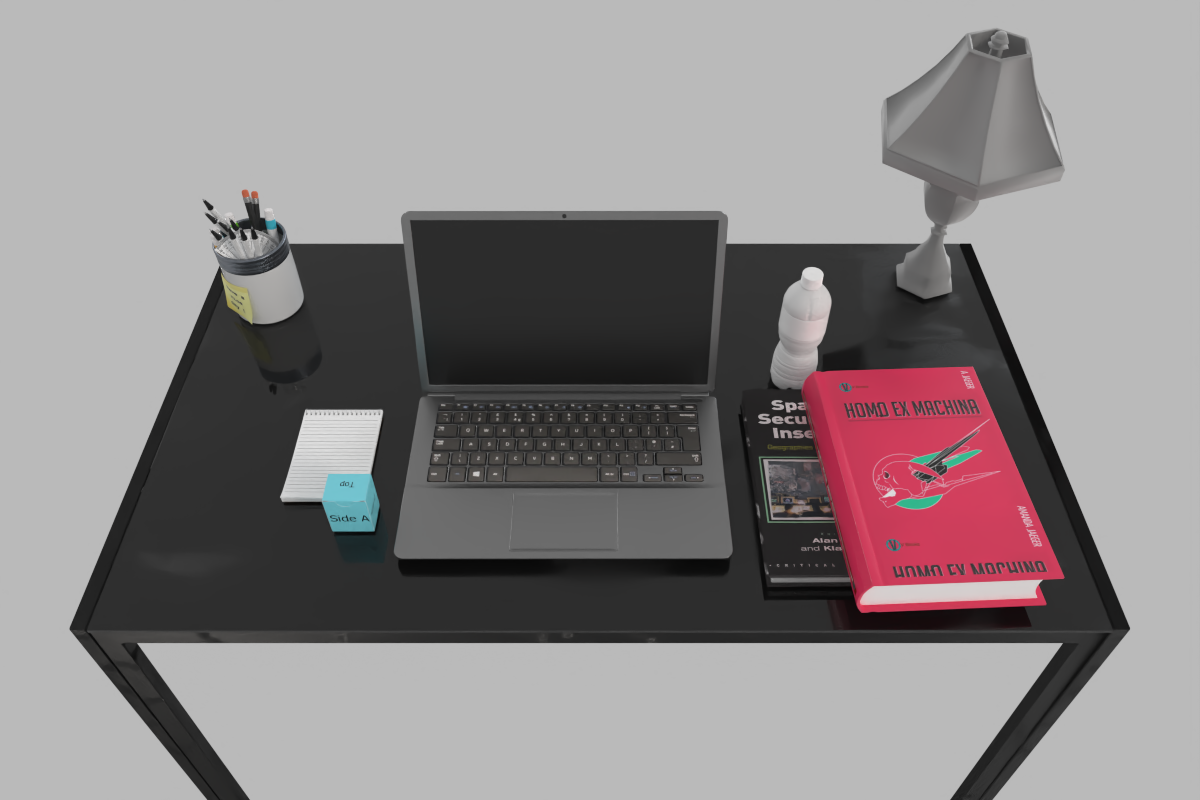
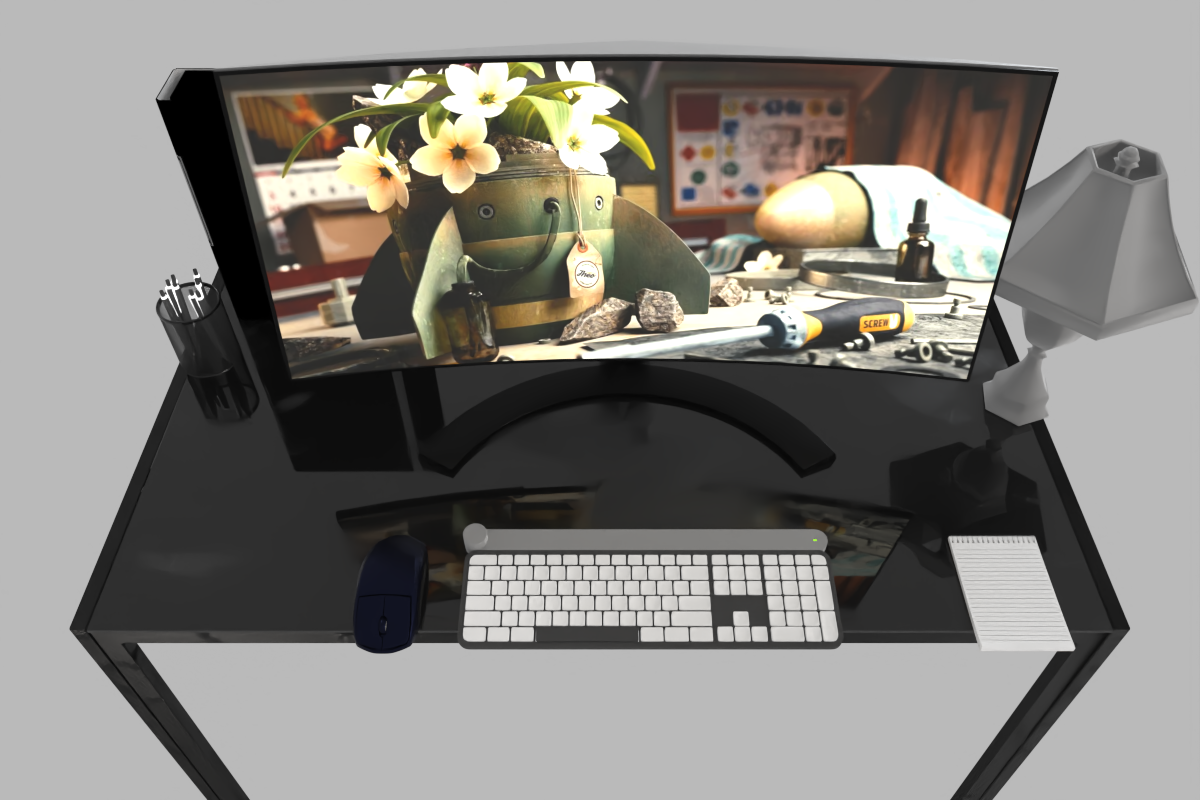
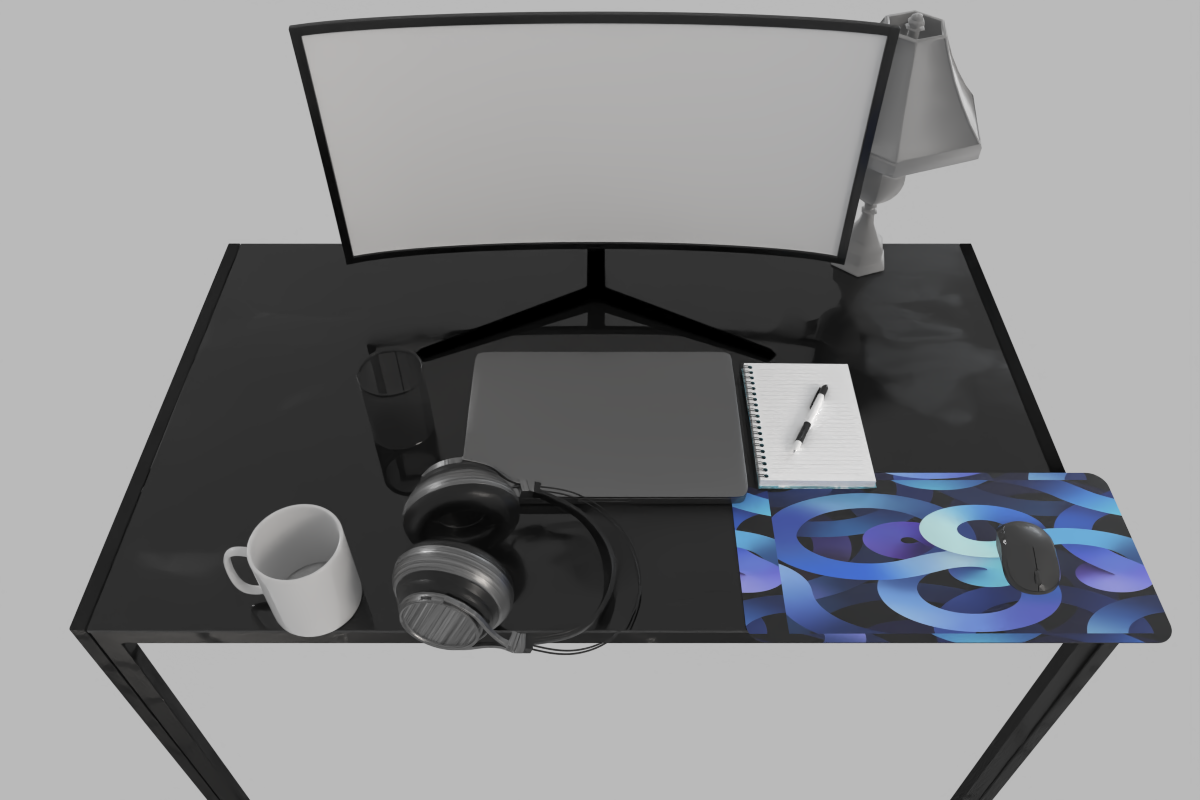



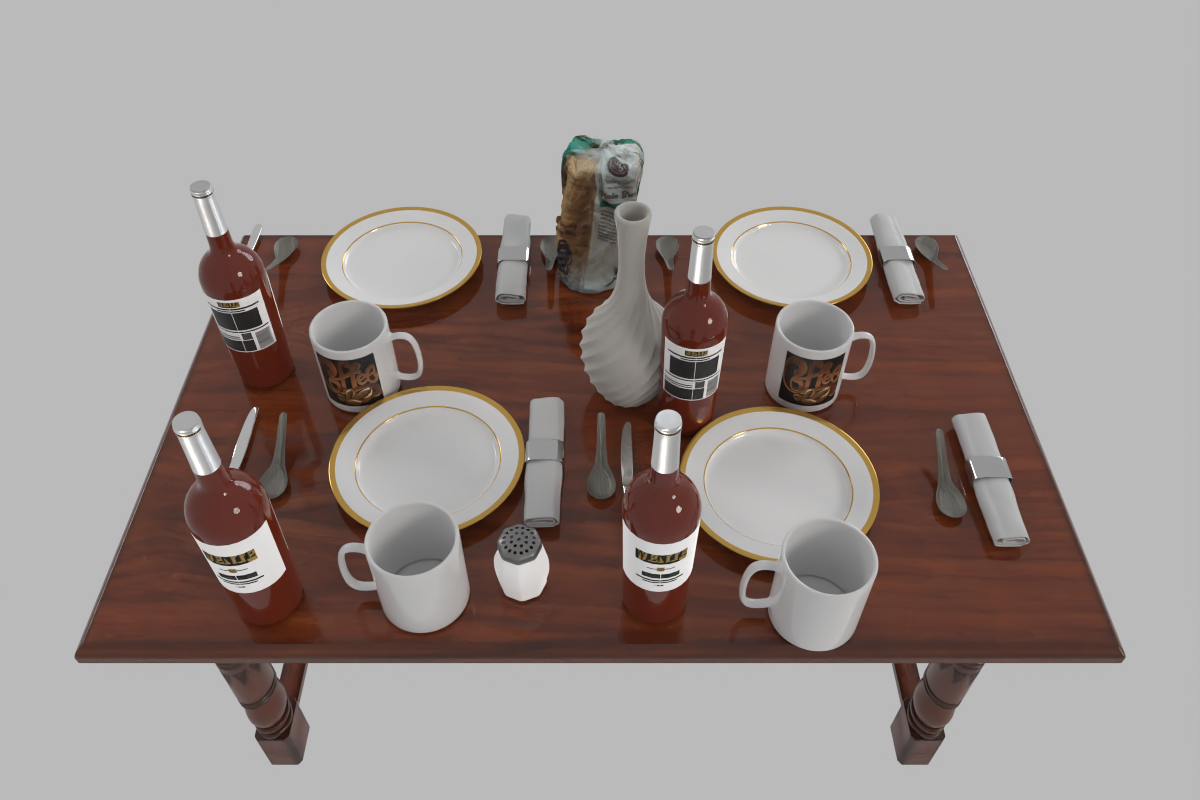
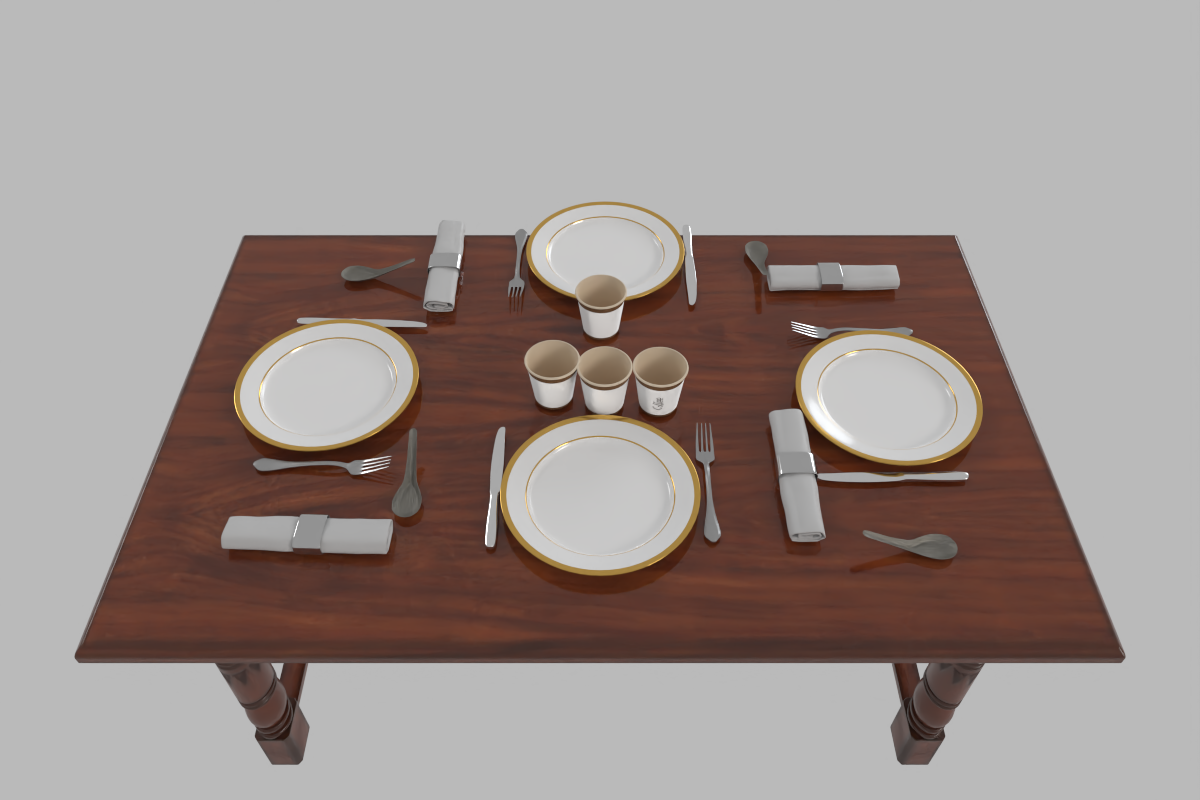
A clustered but organized dining table for 4 people.
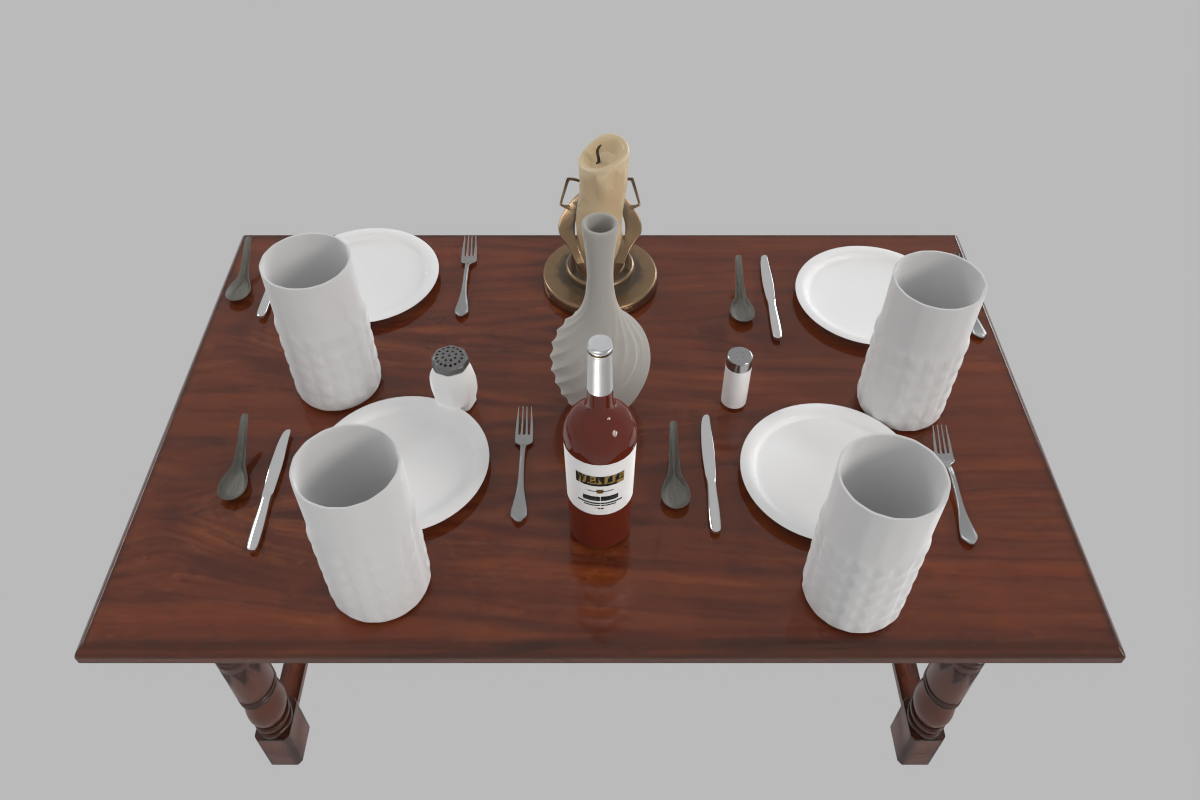



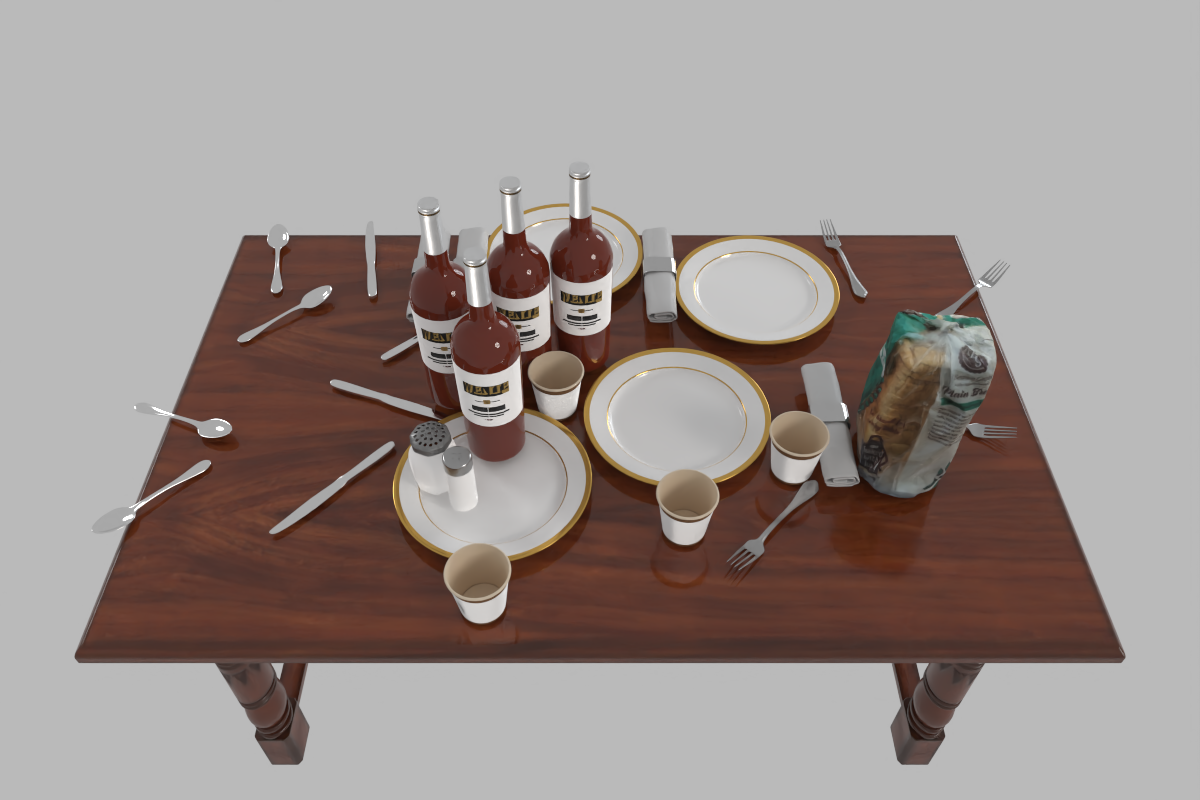
A messy dining table for 4 people.
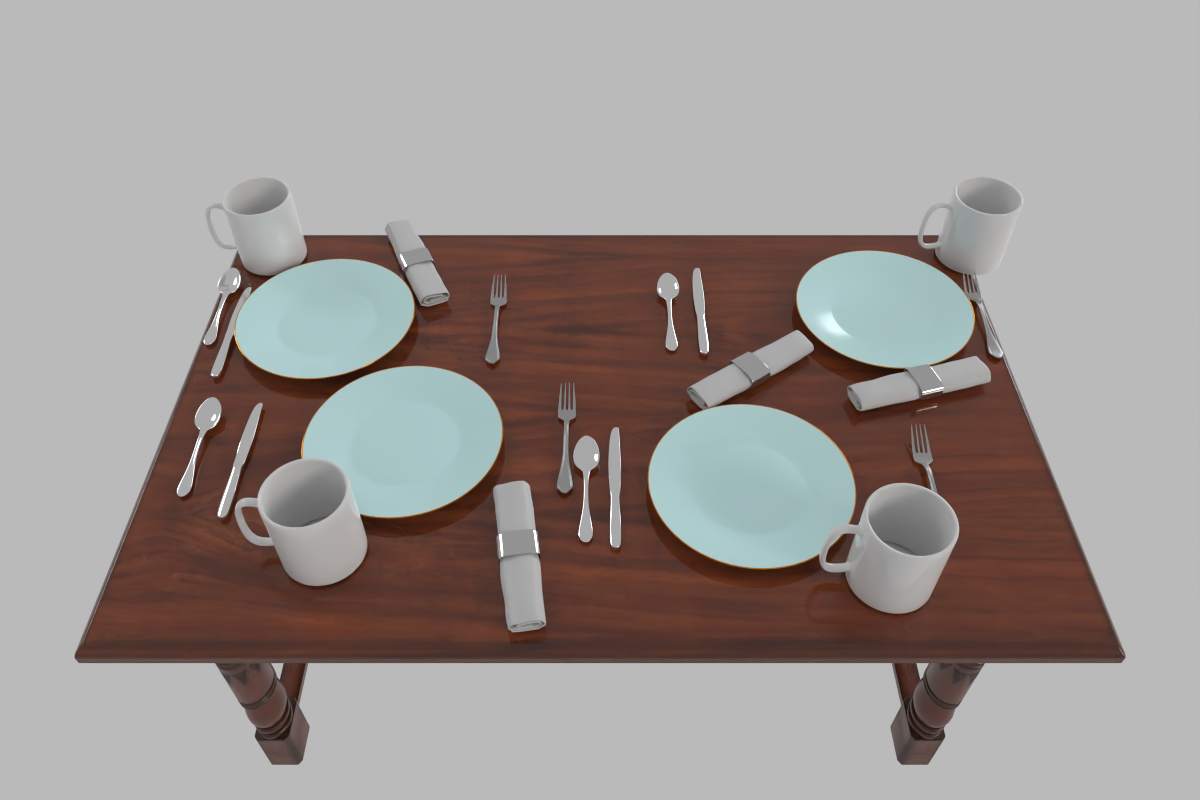
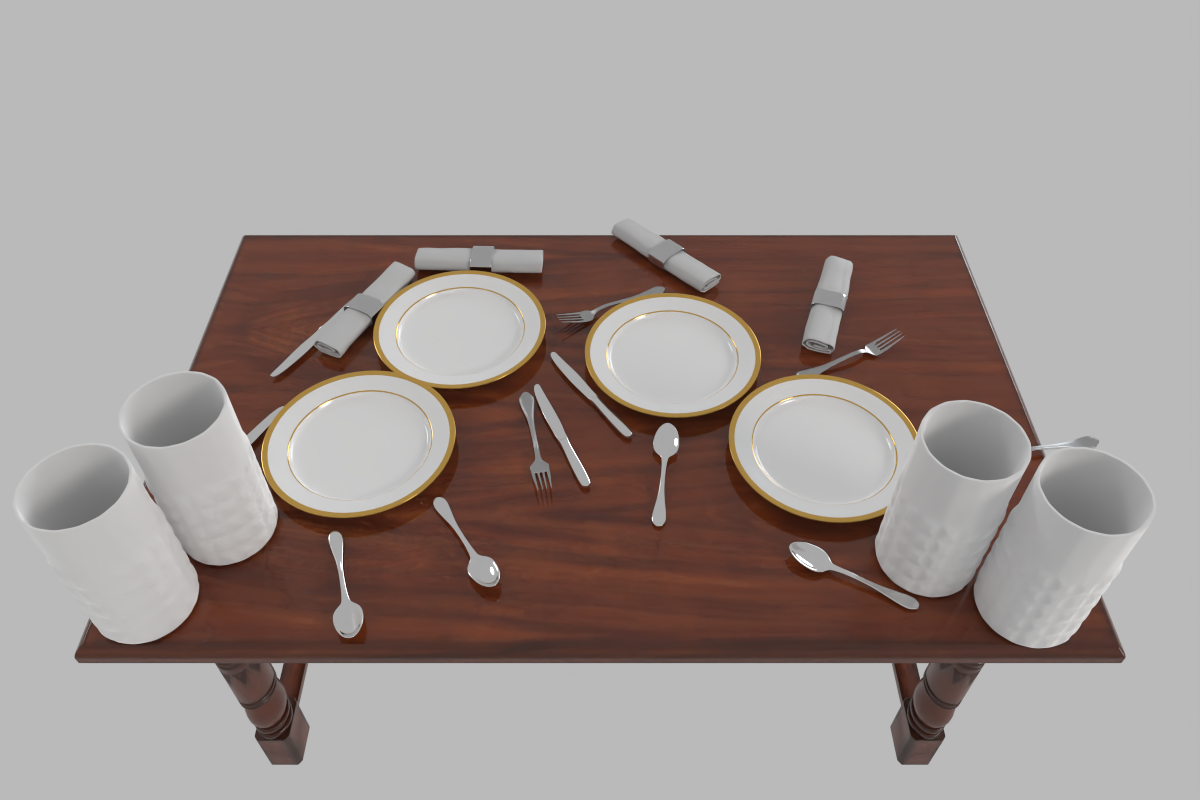



Diverse Scene Generation
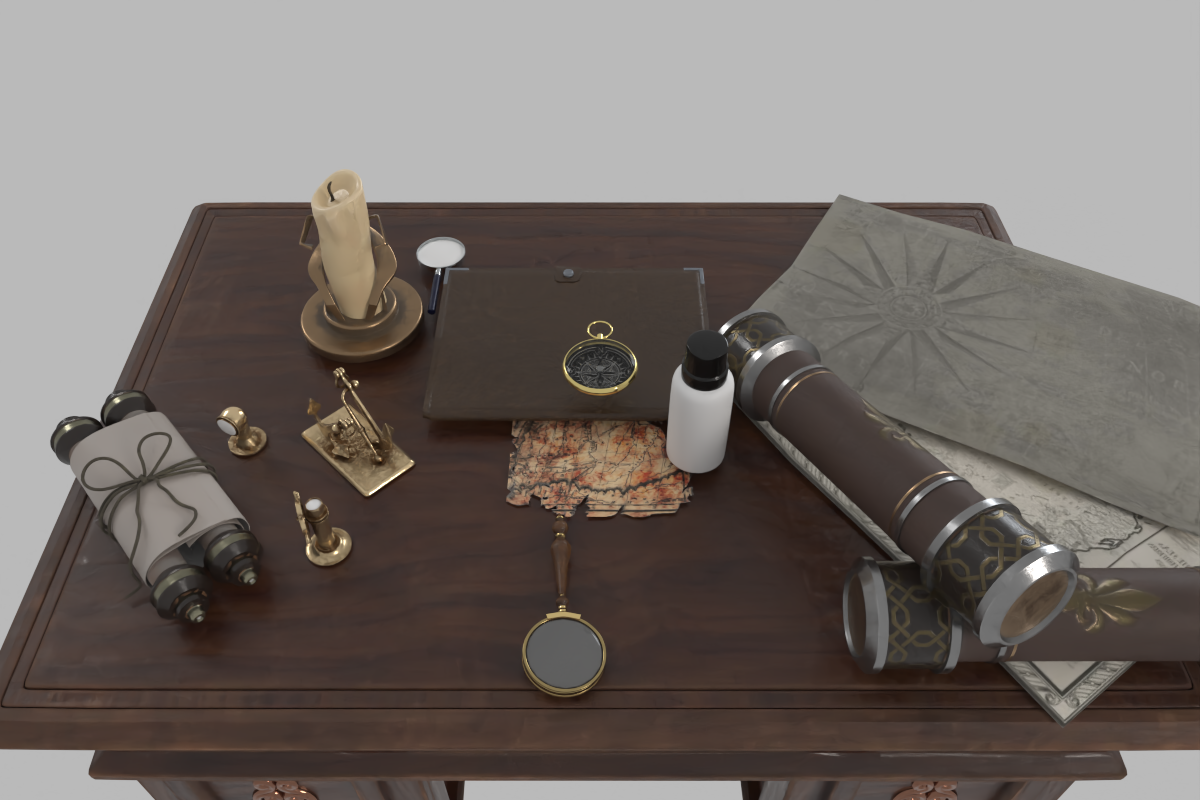
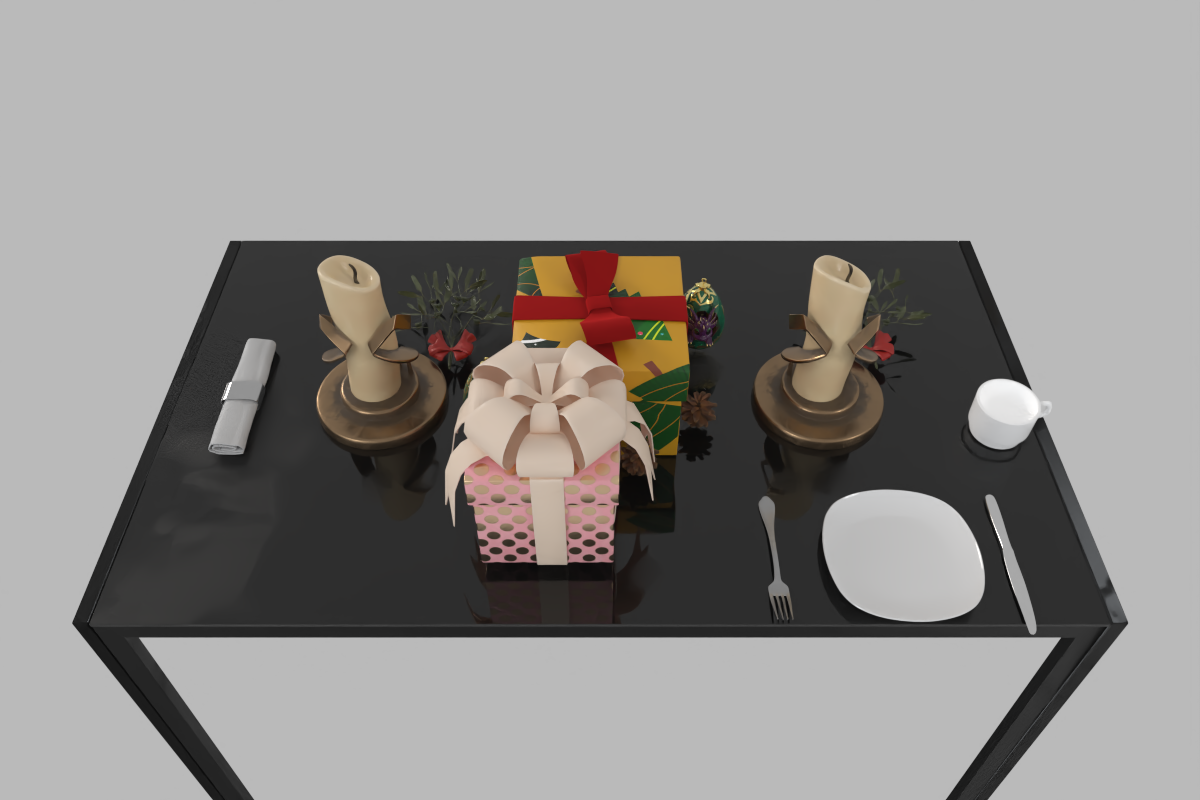
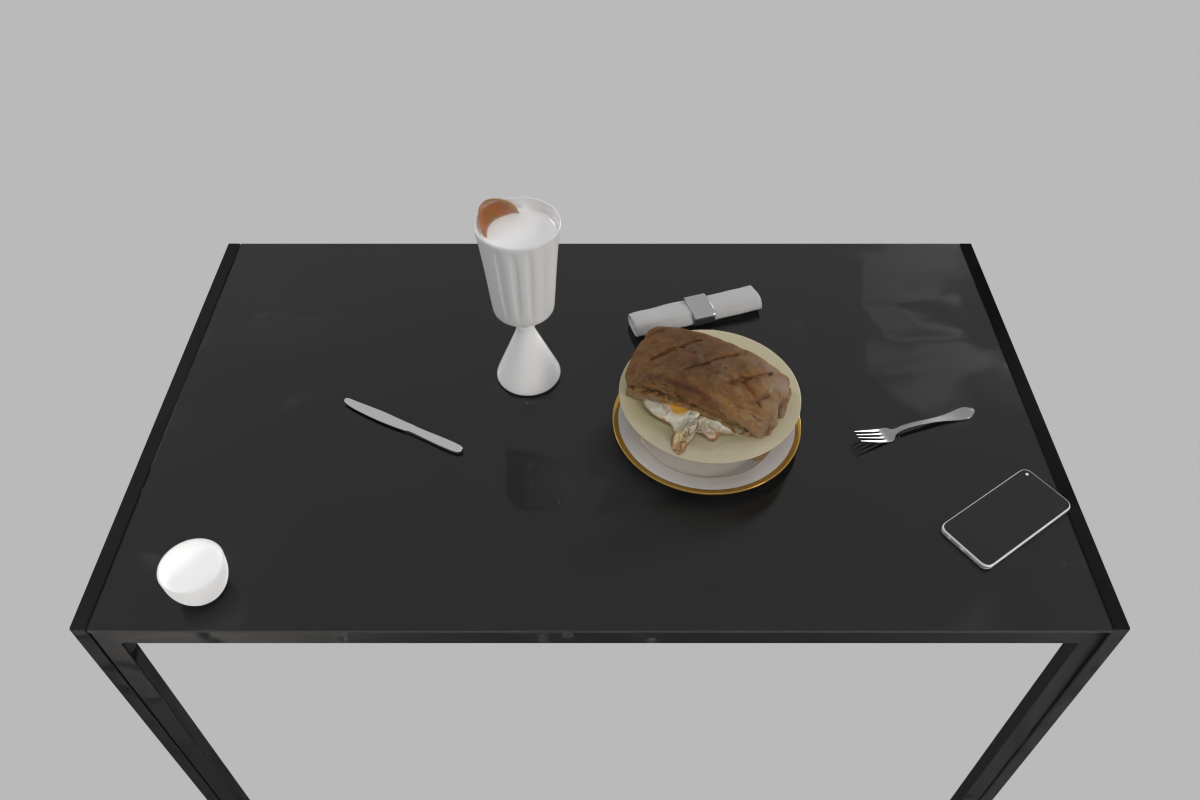
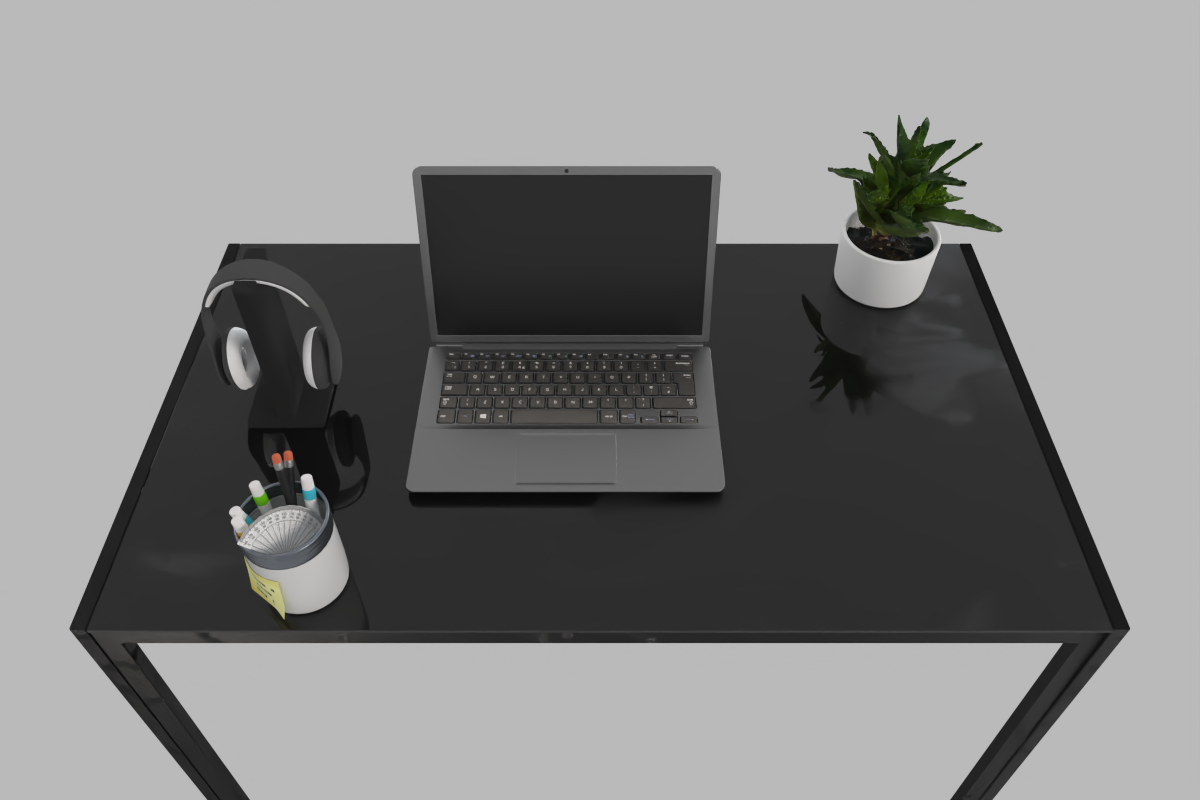






Strong Adaptability
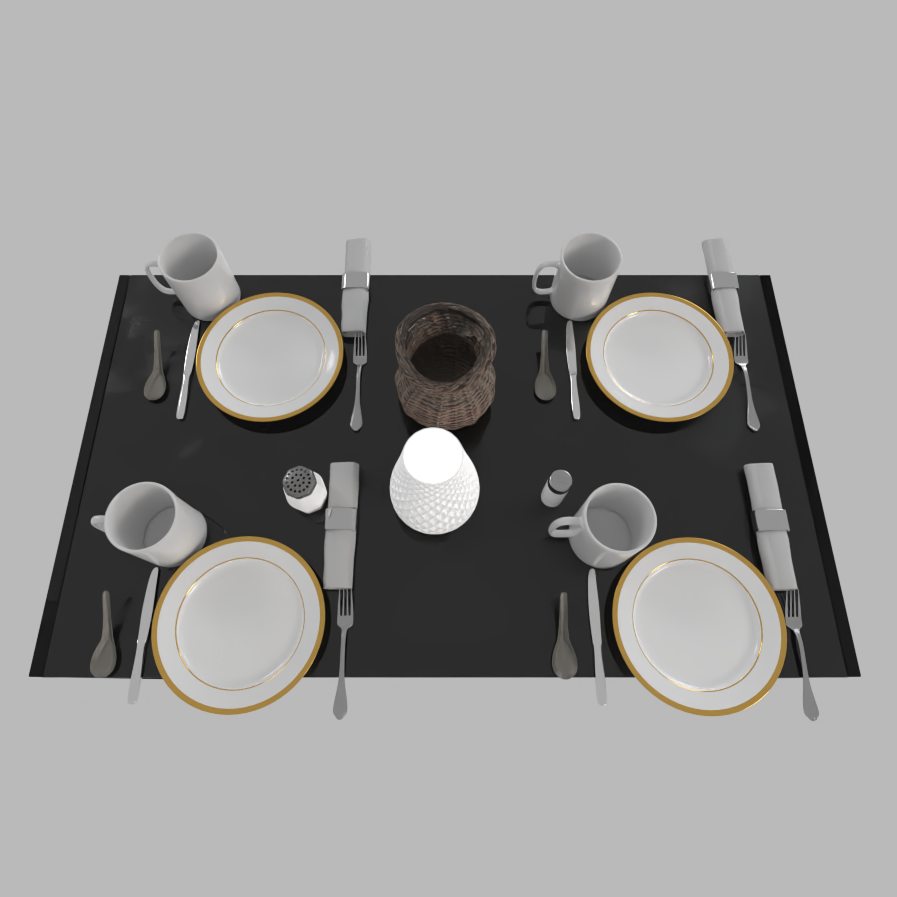
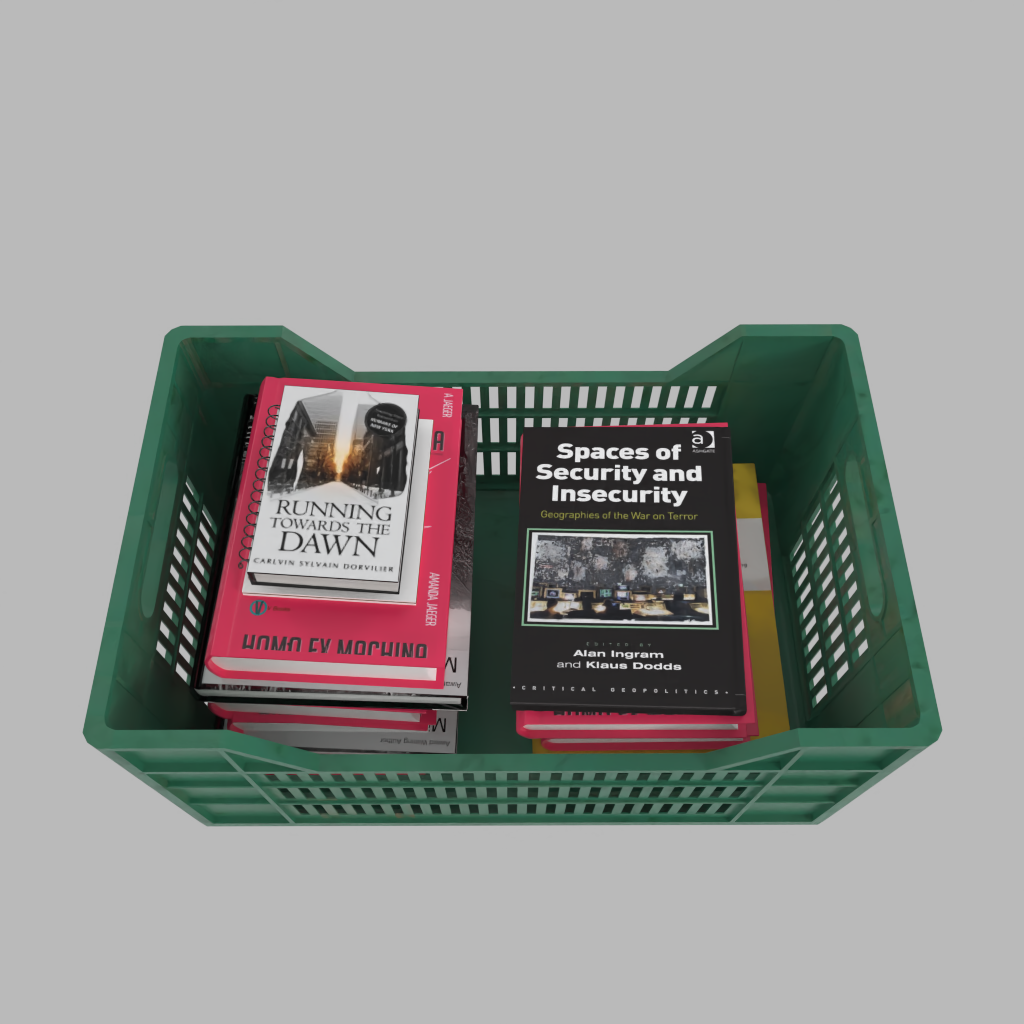




Iterative Scene Generation
A basket full of randomly placed boxes and cans.
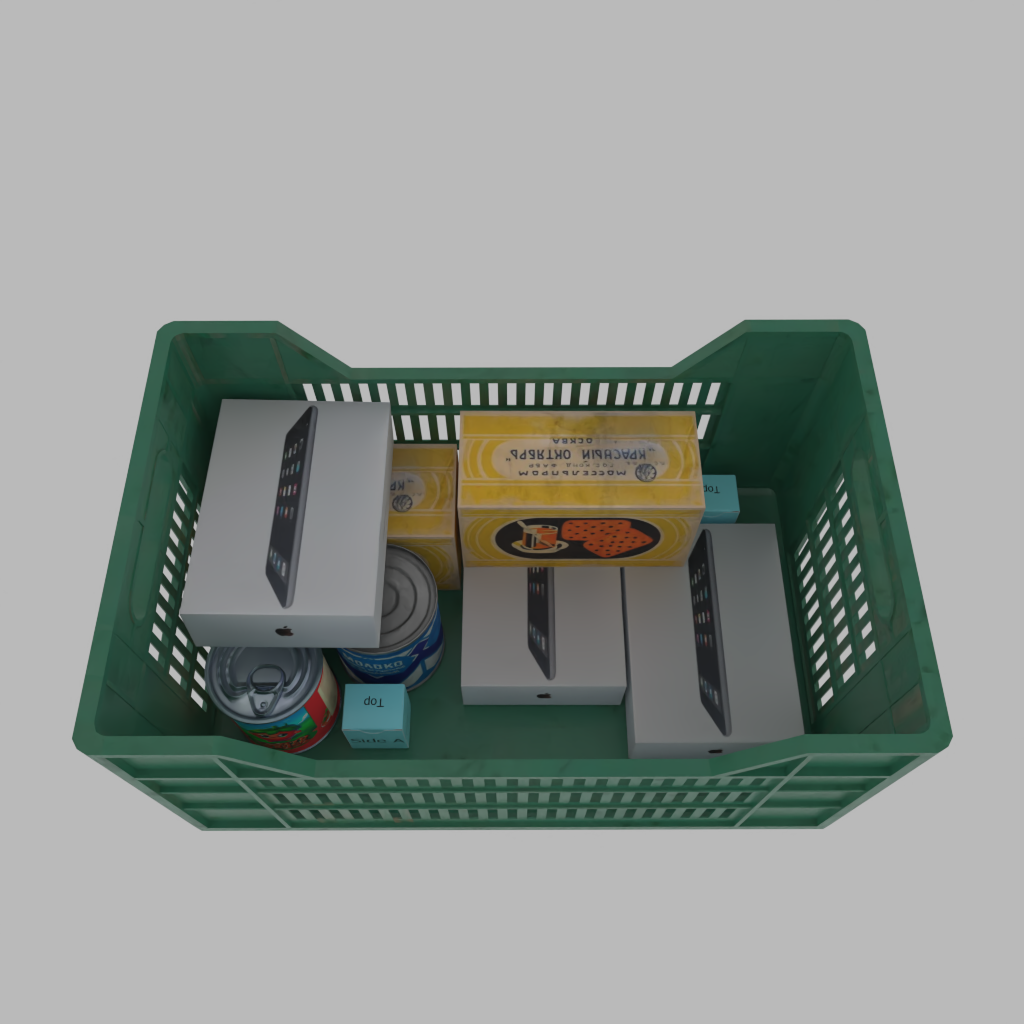
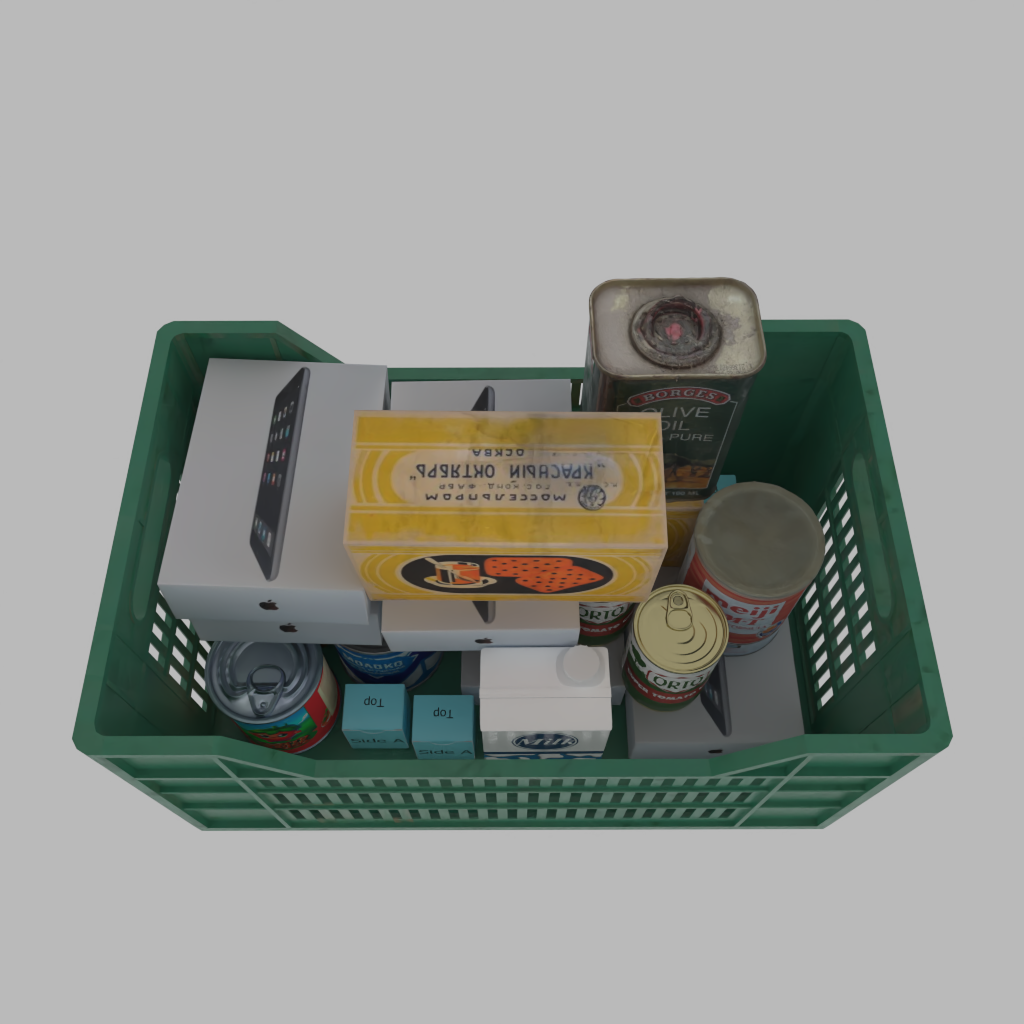
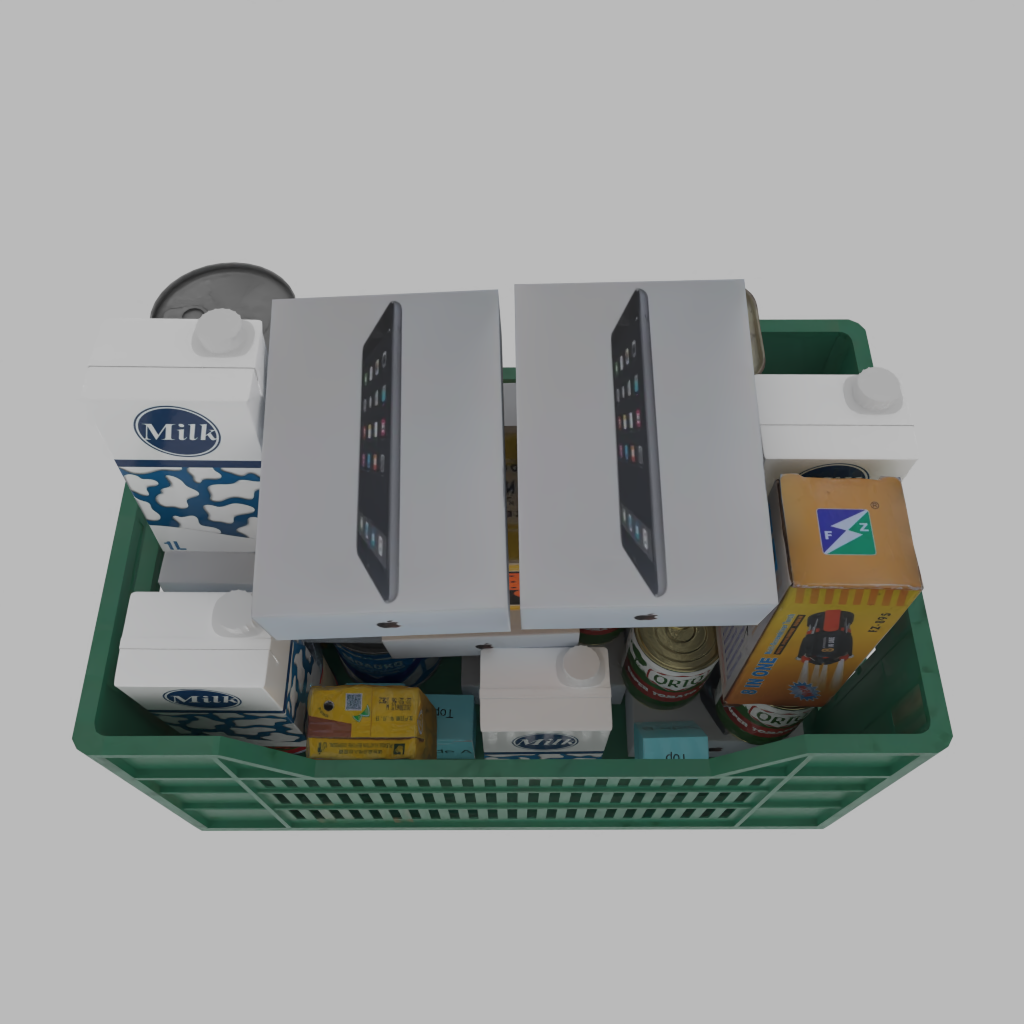
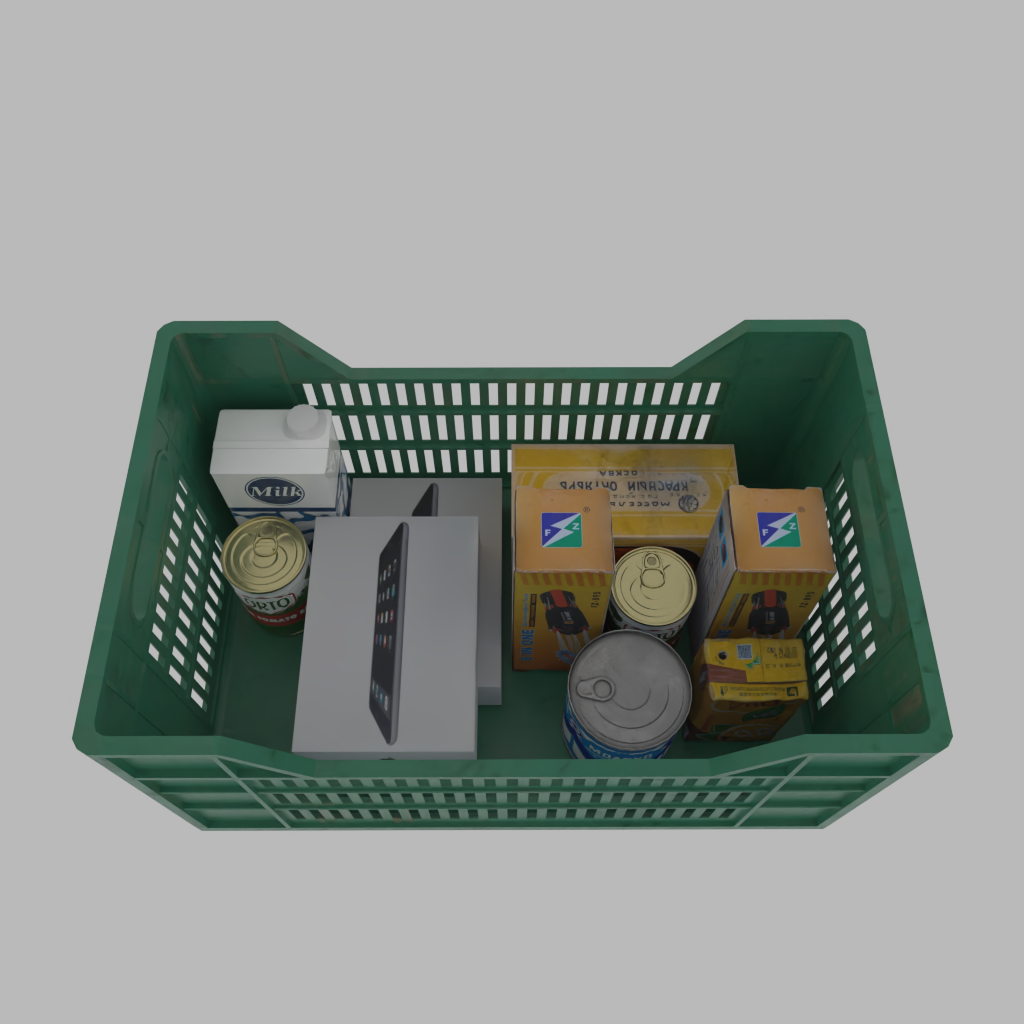
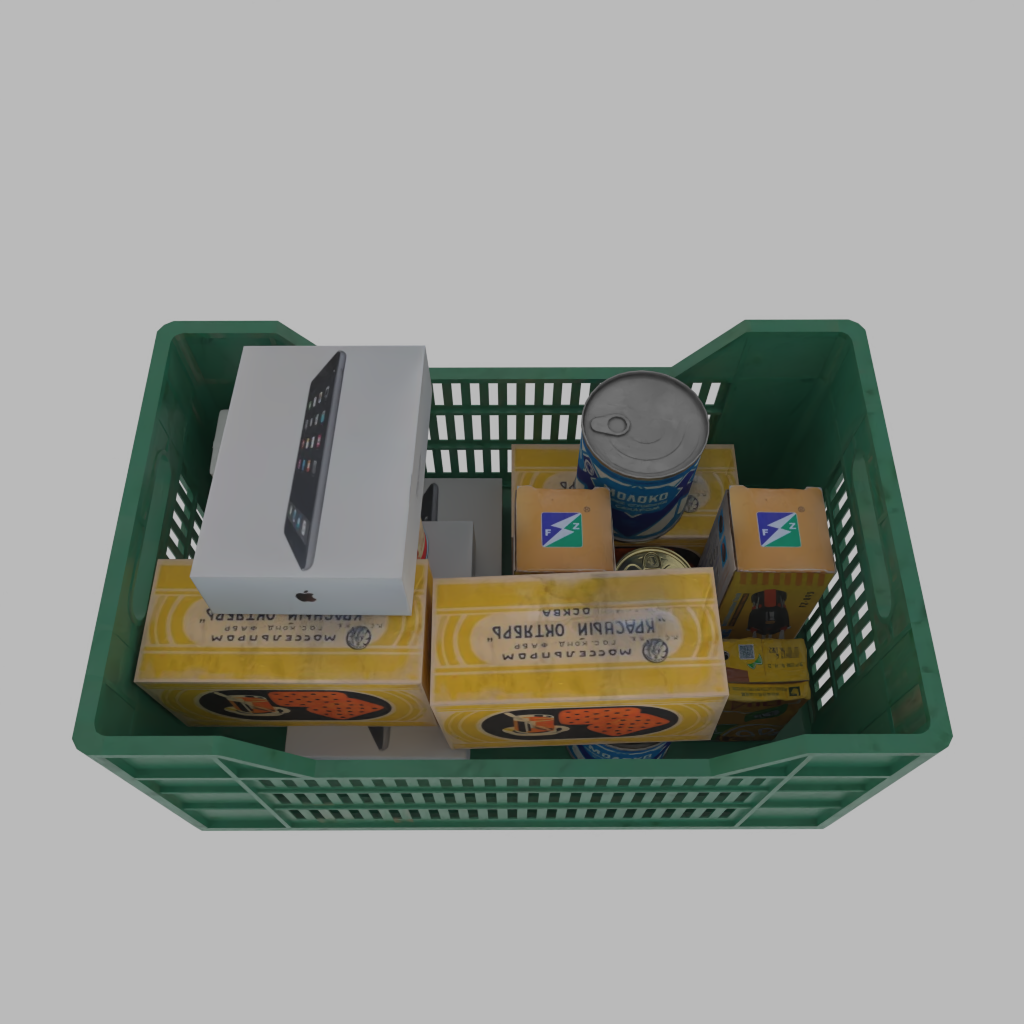
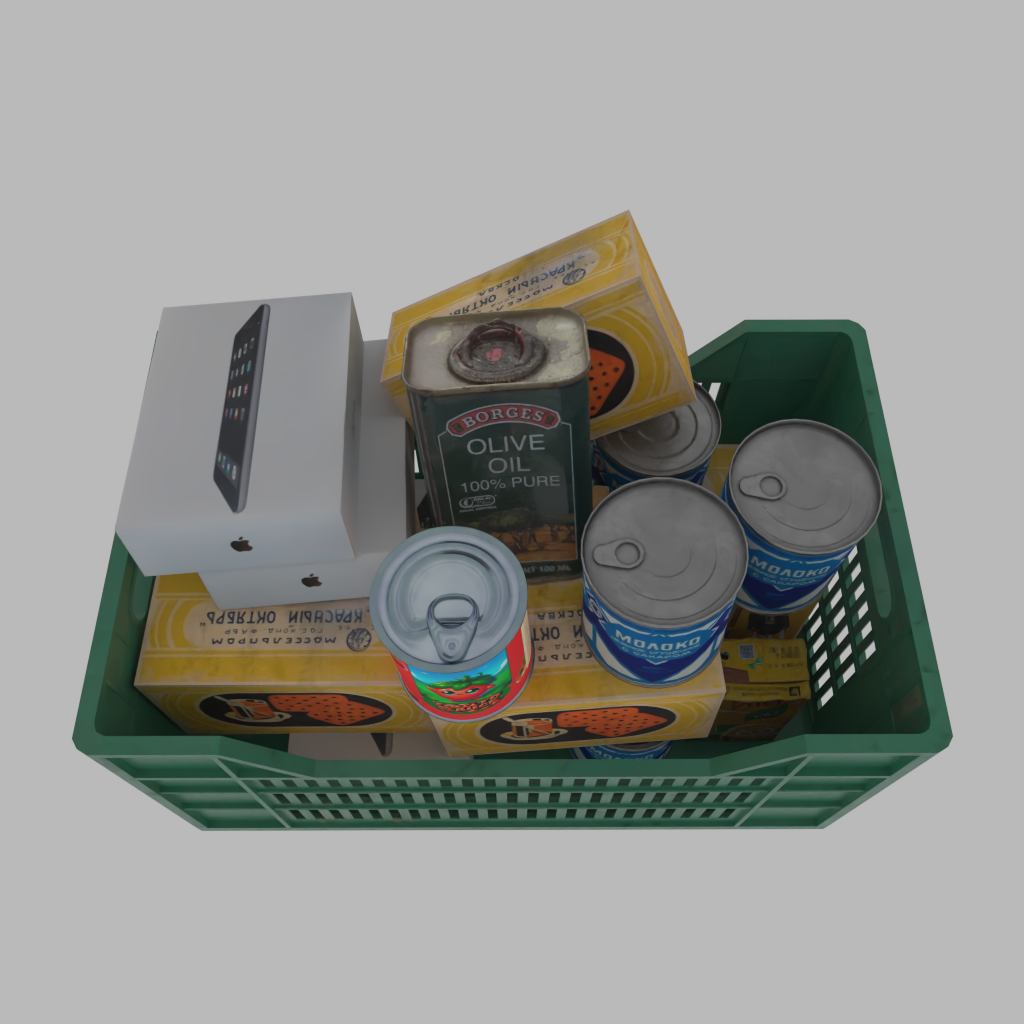








A basket full of randomly placed boxes and cans.
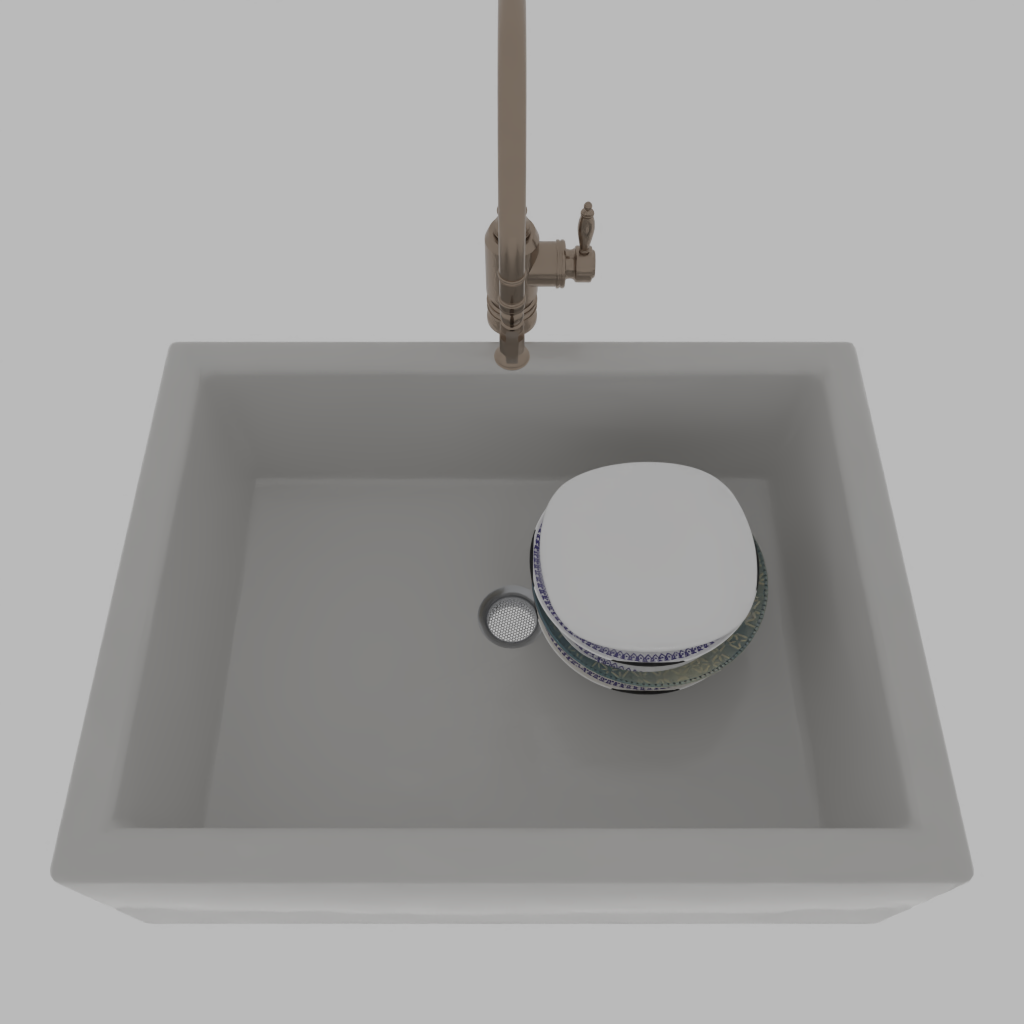
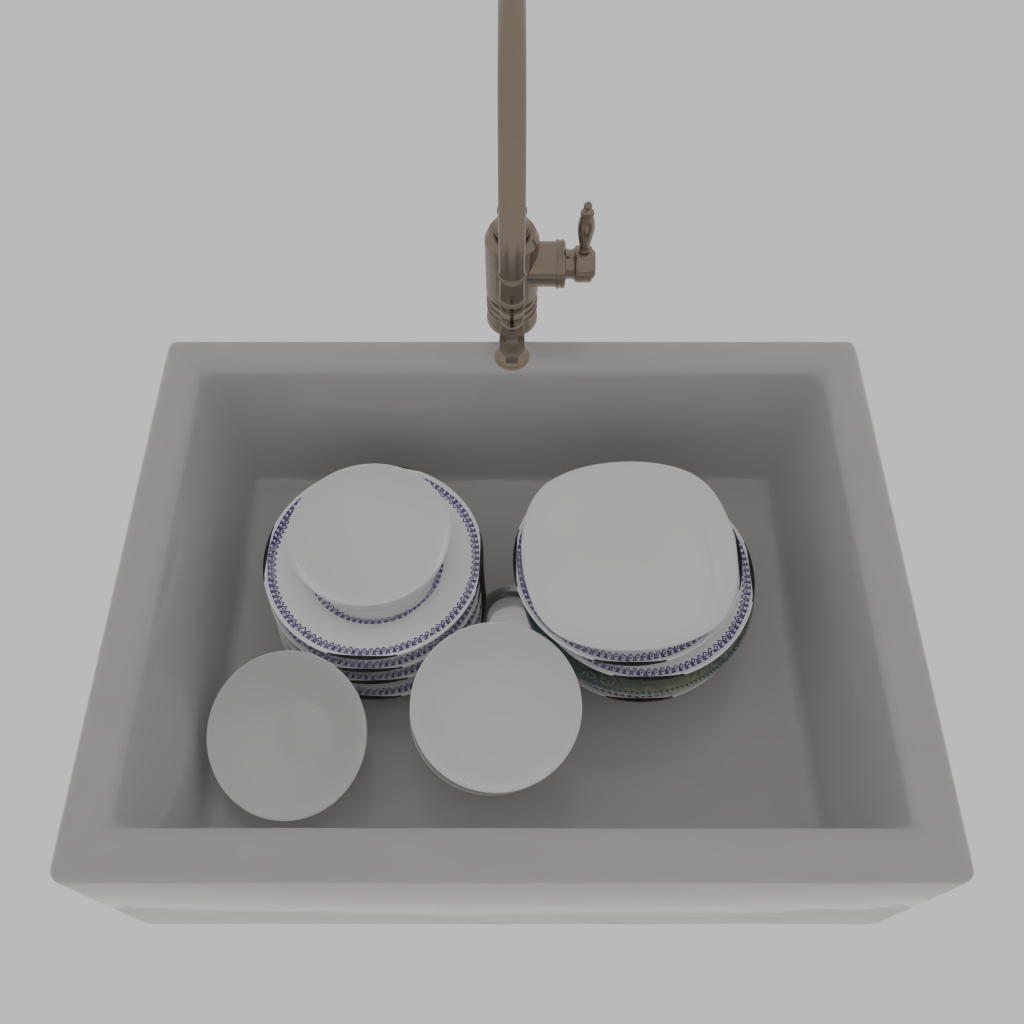
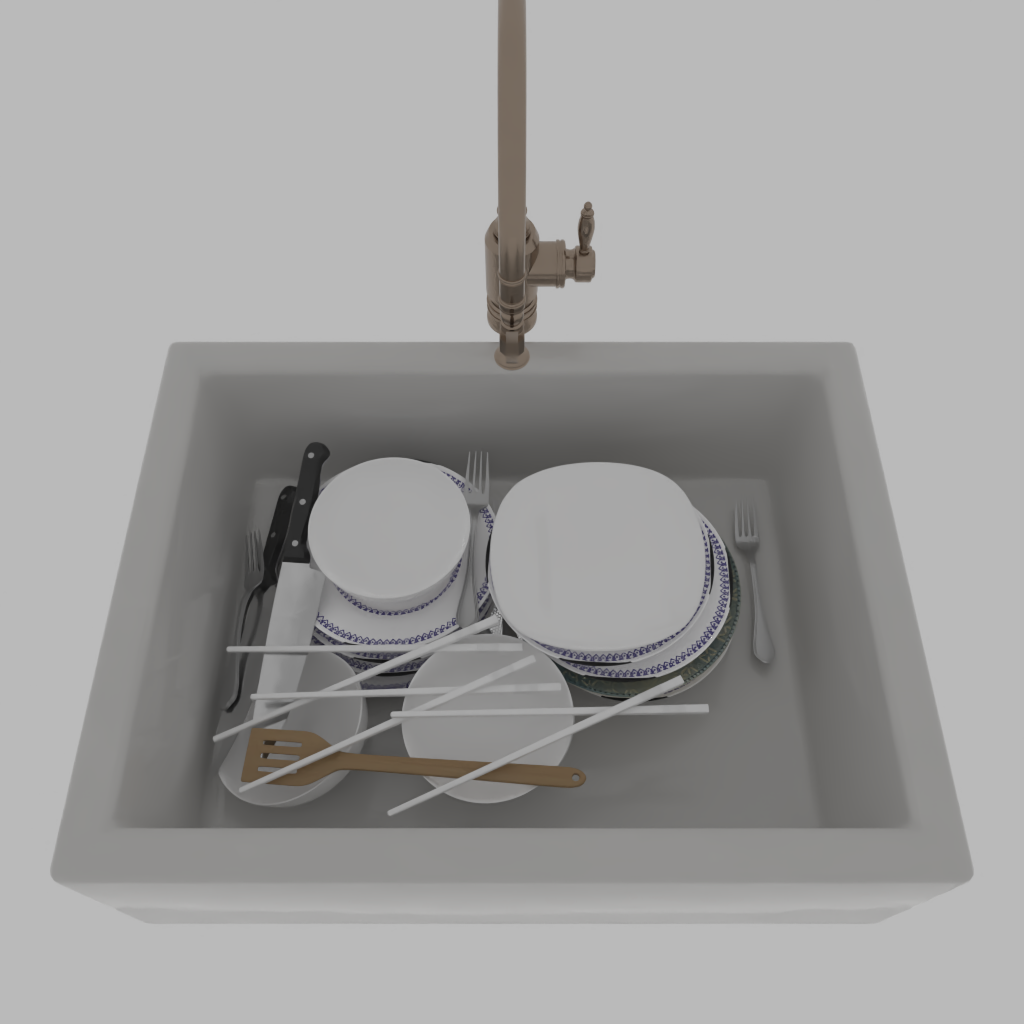

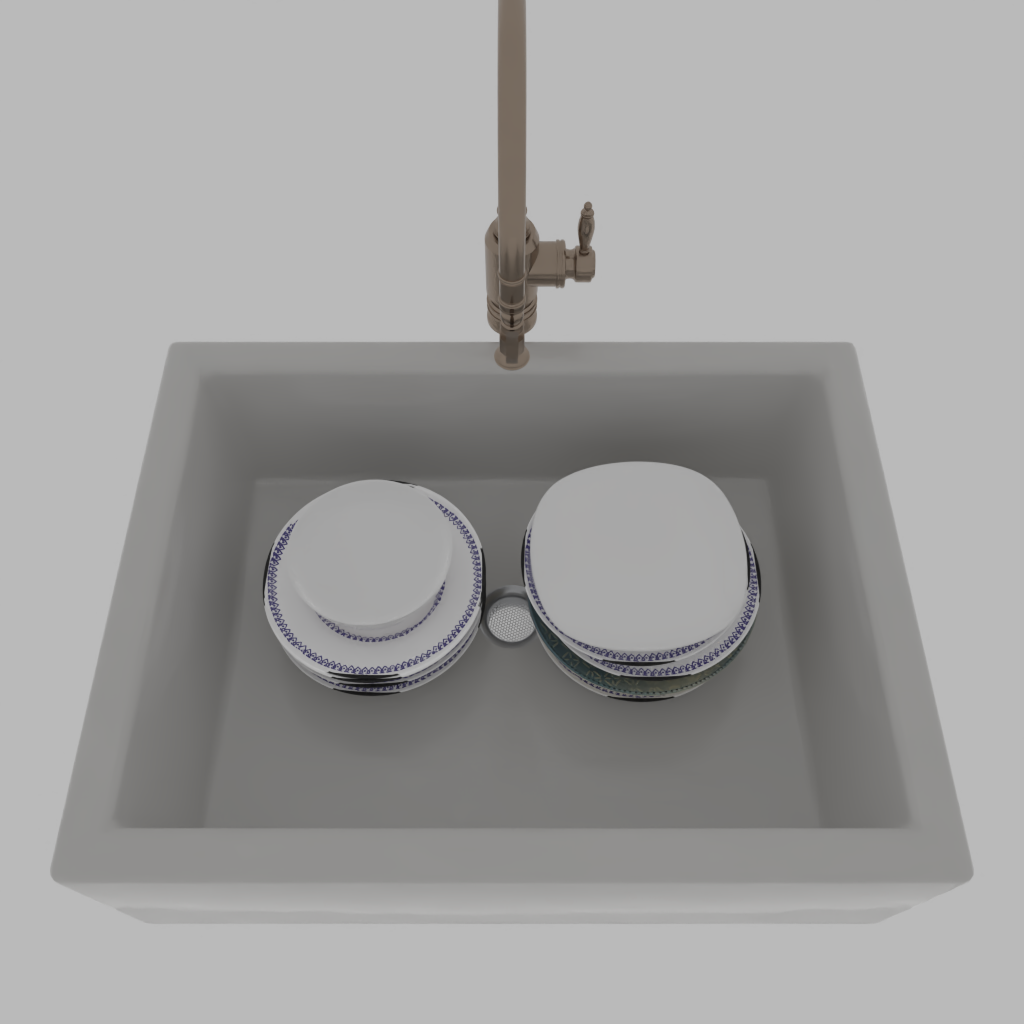


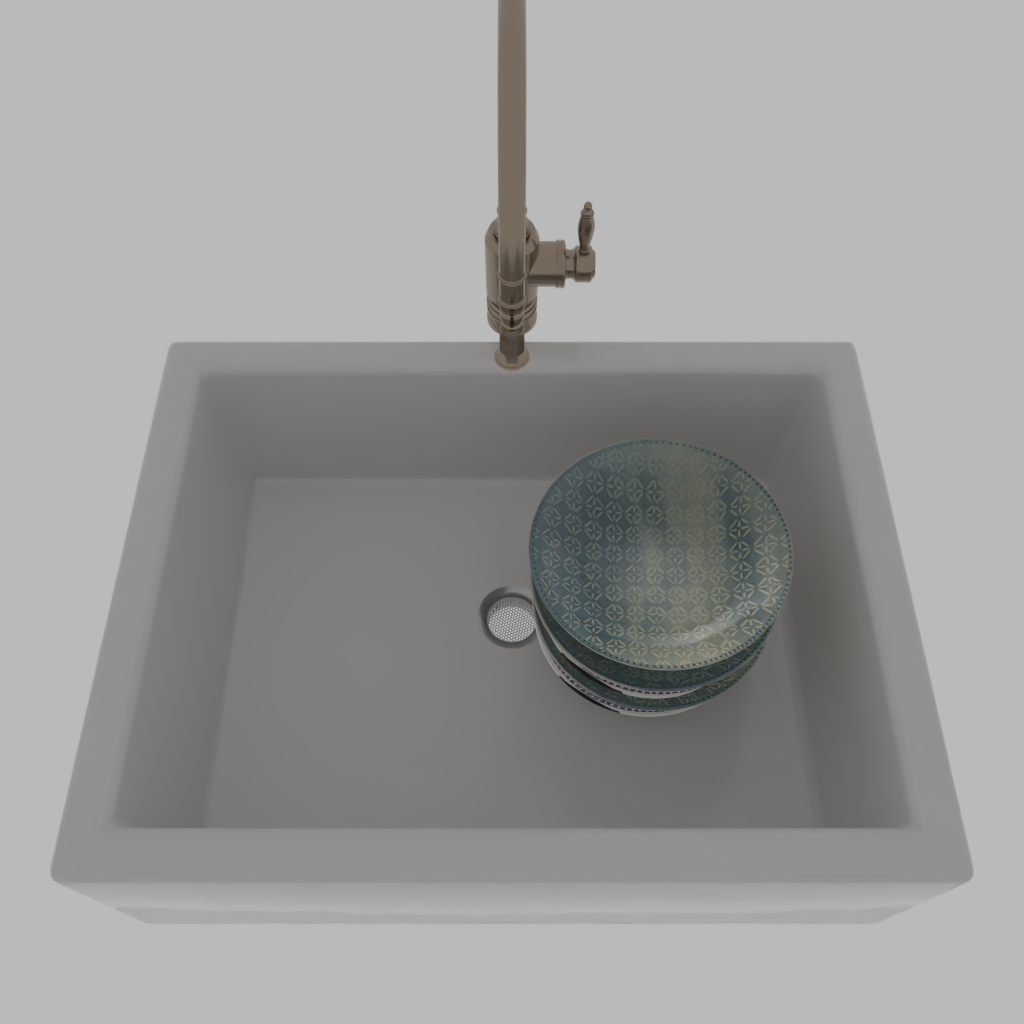
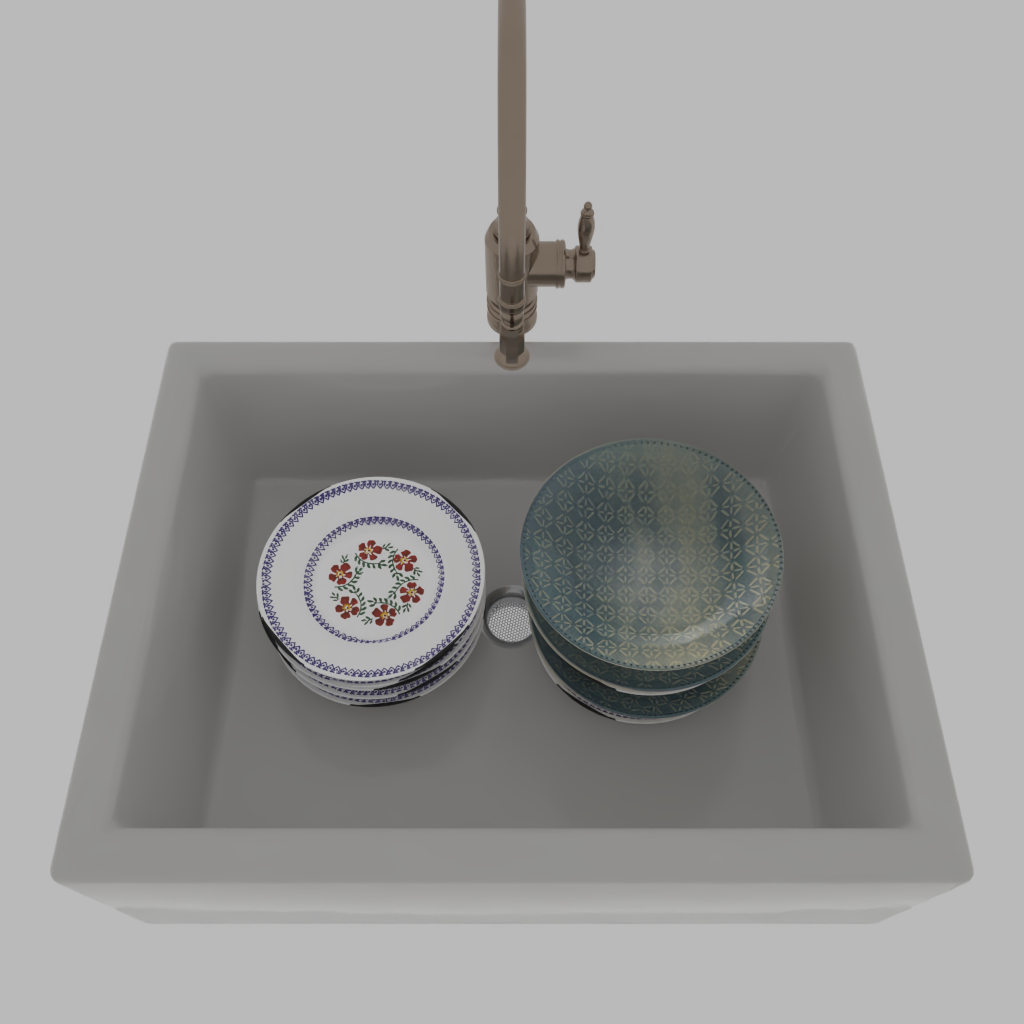
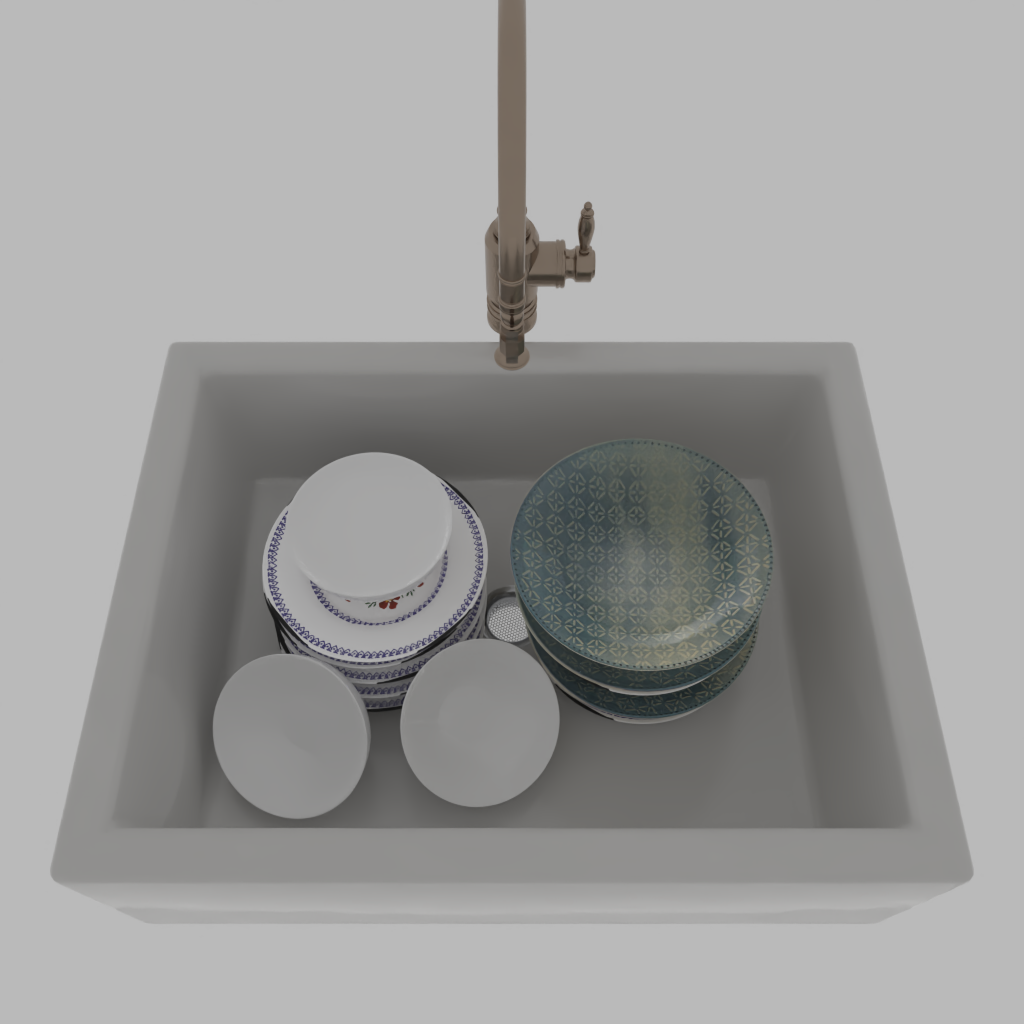
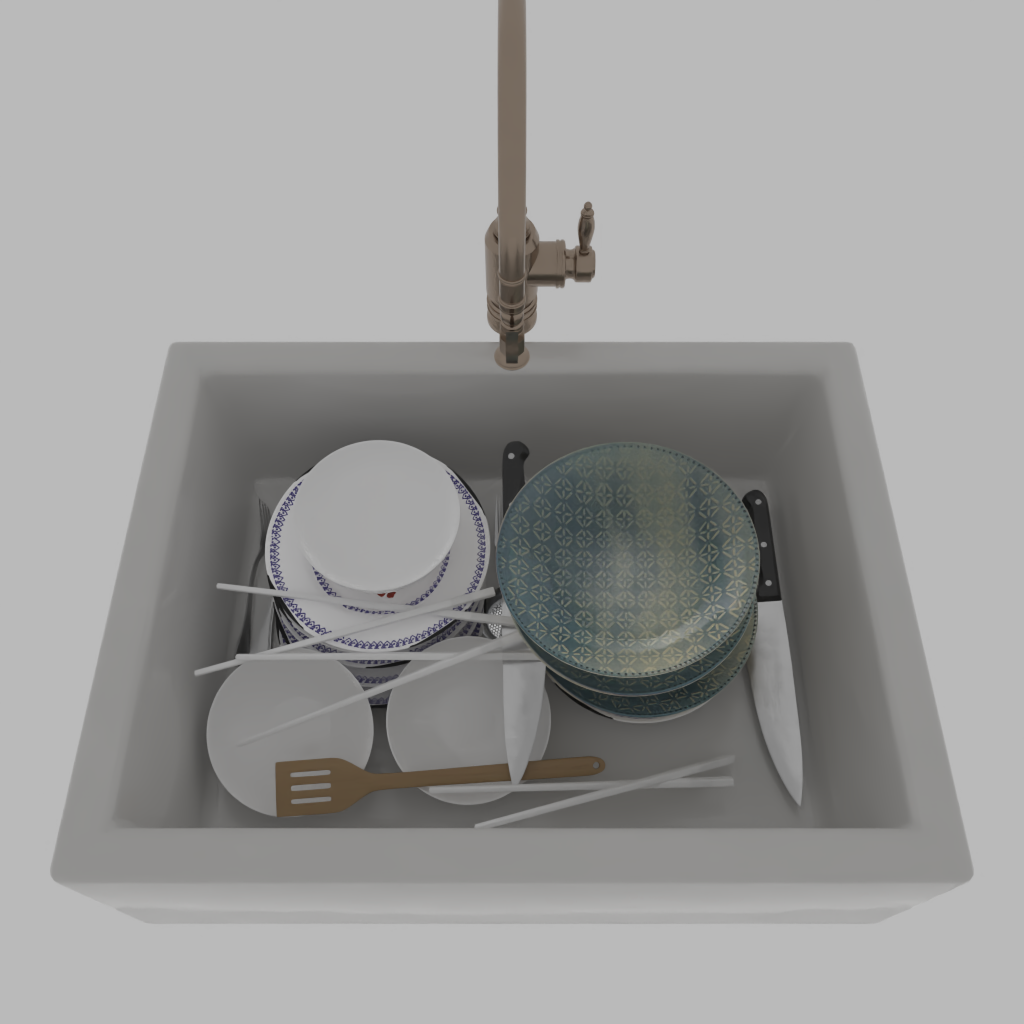
Stability Control with Probabilistic Programming



